Fundamental study of commercial polylactic acid and coconut fiber
4.7 (179) · € 16.99 · In Magazzino

This study aims to provide an alternative fully green biodegradable<?index value="biodegradable"?> 3D printing<?index value="3D printing"?> filament<?index value="3D printing filament"?> other than polylactic acid (PLA)<?index value="Polylactic Acid (PLA)"?> with better properties and lower prices using a fully environmentally friendly process. Two filaments [polylactic acid (PLA) and polylactic acid/coconut fiber (PLA-CF)<?index value="Polylactic Acid/Coconut fiber (PLA-CF)"?>] to be purchased and used to prepare a similar samples under the same conditions which to undergo the same testing to obtain and compare their properties as well as for further comparison with other filaments. The samples are to be designed using SOLIDWORKS<?index value="SOLIDWORKS"?> software according to the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM)<?index value="American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM)"?>standards. The prepared designs are then to be converted to gcode using CURA software. FDM Creality 3D printer (Model: CR10S-PRO) to be used printing a set of specimens for each required test. The prepared samples then undergo several mechanical tests to specify their exact properties. PLA 3D filament<?index value="filament"?> roll had been purchased from Fabbxible Technology; Crystallized nature based NatureWorks made from corn starch. While Magma PLA-CF roll had been purchased from 3D Gadgets Malaysia. Both rolls had an average diameter of 1.75 mm and average length of 300 m.

Various Types of Natural Fibers Reinforced Poly-Lactic Acid Composites

Three main reactions of PLA in the presence of MA and peroxide; a

A review on degradation mechanisms of polylactic acid: Hydrolytic, photodegradative, microbial, and enzymatic degradation - Zaaba - 2020 - Polymer Engineering & Science - Wiley Online Library
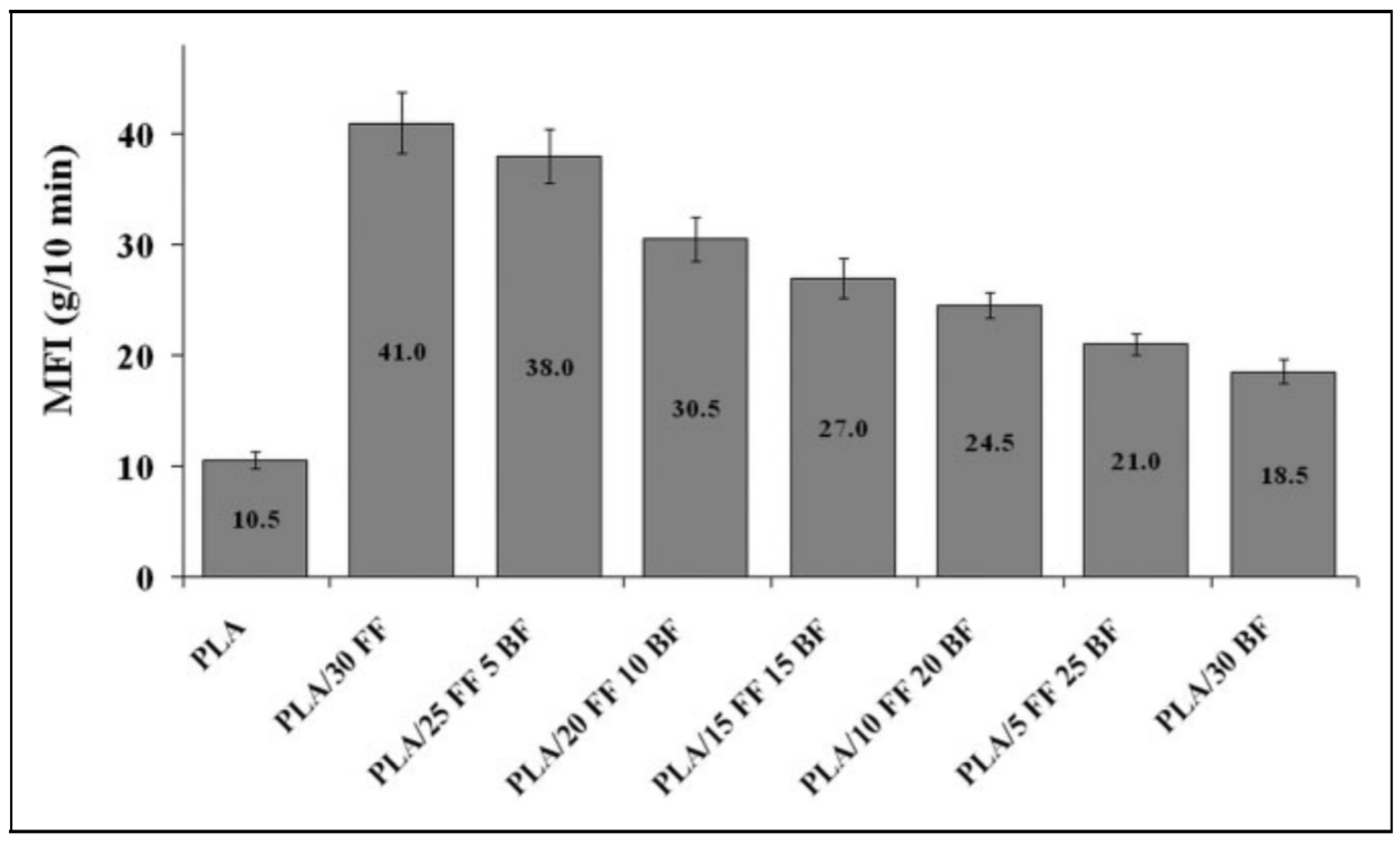
Polymers, Free Full-Text

Proposed schematic mechanism of PLA biodegradation. PLA: poly(lactic acid).

Thermal stability and flammability of coconut fiber reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites - ScienceDirect

Preparation and mechanism of lightweight wood fiber/poly(lactic acid) composites - ScienceDirect

Properties of coir fibre/polylactic acid composites based on amylase processing - Zhicheng Sun, Xingxing Yang, Min Wang, Guoyan Duan, Wei Wang, 2024

Polymers, Free Full-Text

PLA based biocomposites for sustainable products: A review - ScienceDirect

What is PLA? (Everything You Need To Know) - TWI

Polylactic acid (PLA) biocomposites reinforced with coir fibres: Evaluation of mechanical performance and multifunctional properties - ScienceDirect
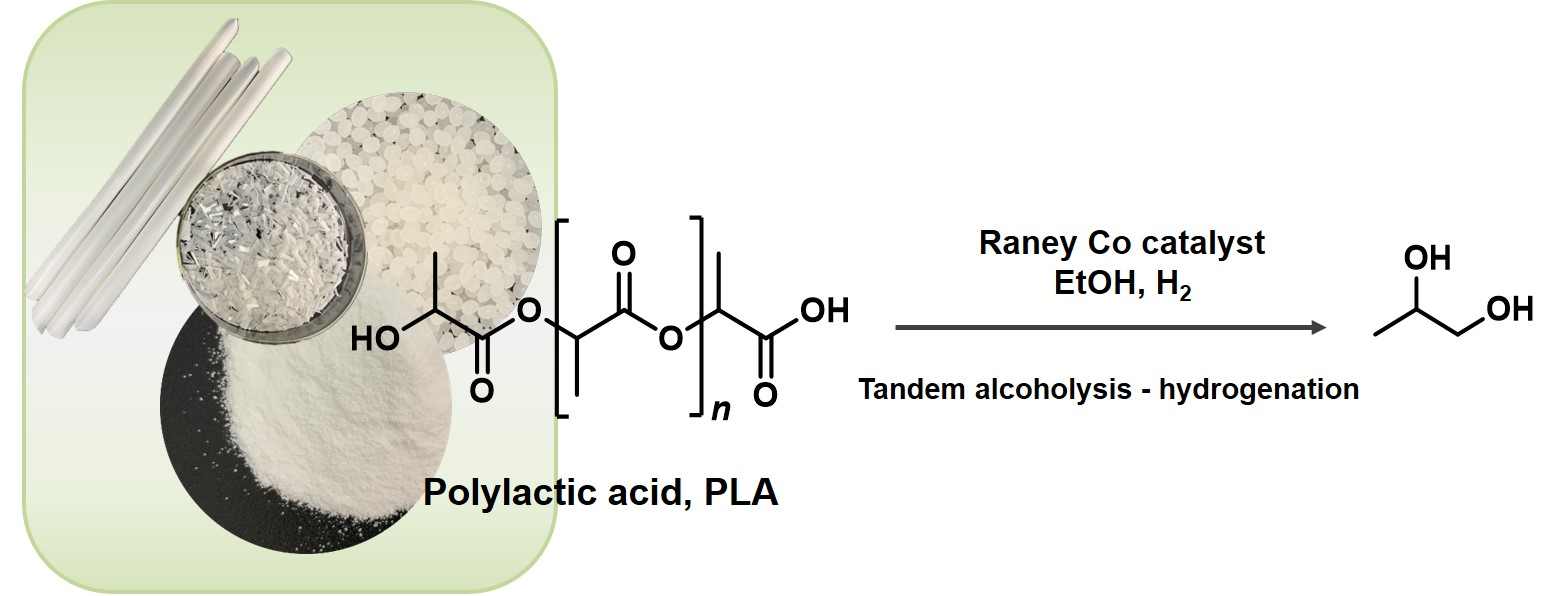
Polymers, Free Full-Text






